Cloud computing is a type of service that provides shared access to remote servers and data over the internet. It’s an alternative to buying, installing, and maintaining your own computer hardware.
Cloud computing is the most recent trend in IT. It allows users to outsource their work to a remote server, which can be accessed through the internet. This type of outsourcing has many benefits, such as lower fees and faster speeds.
Cloud computing: the term in the boardroom that you still pretend to understand.
Fortunately, it’s a very straightforward concept, although technically challenging. On the surface, cloud computing seems to be simply another method for people to pool resources and boost output.
When you utilize cloud computing, you’re basically outsourcing a computer-related job in the same way that a business would outsource accountancy, manufacturing, customer service, or human resources, to mention a few.
Instead, activities like data storage, web server hosting, Bitcoin mining (warning), and software maintenance are outsourced via cloud computing.
What’s the big deal about this?
Let’s use the example of two comparable e-commerce companies to better appreciate the benefits of cloud computing. Both companies sell a product and use the internet to do it. Both are young companies with a limited client base, but they may fairly anticipate their e-commerce store’s traffic to grow in the future.
The first company, Tod’s Toys, runs its website on locally installed servers and manages all of its own data. But don’t worry: Tod’s Toys has an outstanding CTO in charge, and the existing hardware/software stack is operating well.
The second company, Gupta’s Guitars, is a bit more unique, and they chose to put their website on a cloud server instead. Gupta’s Guitars also has a competent CTO who keeps an eye on the health of the internet shop.
Tod’s Toys and Gupta’s Guitars are seeing comparable traffic rates in their early phases. Tod’s Toys, on the other hand, is experiencing a greater operational cost as a result of their web servers, which they have more than they need. The toy shop, on the other hand, is unconcerned since they anticipate traffic to exceed their server capacity.
Gupta’s Guitars, on the other hand, paid ad hoc for their server use. The guitar shop hasn’t seen any waste since their server access scales with traffic. In fact, since their traffic volume was modest, their cloud server costs were cheap as well. With their funds, they naturally hosted a guitar-fueled pizza party!
Both online shops see a sharp increase in volume and sales, as expected. Gupta’s Guitars is overjoyed and will most likely host another pizza party. Tod’s Toys, on the other hand, does not have nearly as much time to rejoice.
As demand for their self-hosted platform outstrips their capacity, the online toy shop rapidly switches to scalable server hardware. Instead of the amazing toys that Tod’s provides, potential buyers are given 404 error messages. *sad expression*
As you can see, cloud computing allowed Gupta’s Guitars to outsource their server requirements and concentrate on other areas of their company as a consequence.
The example is excessively simplified, but the idea is clear.
Cloud Computing Fundamentals
Enterprise cloud computing, like in the following example, is the term used to describe cloud computing for companies. This is in contrast to other cloud computing services such as Google Drive or MegaUpload, which are more consumer-oriented (R.I.P.).
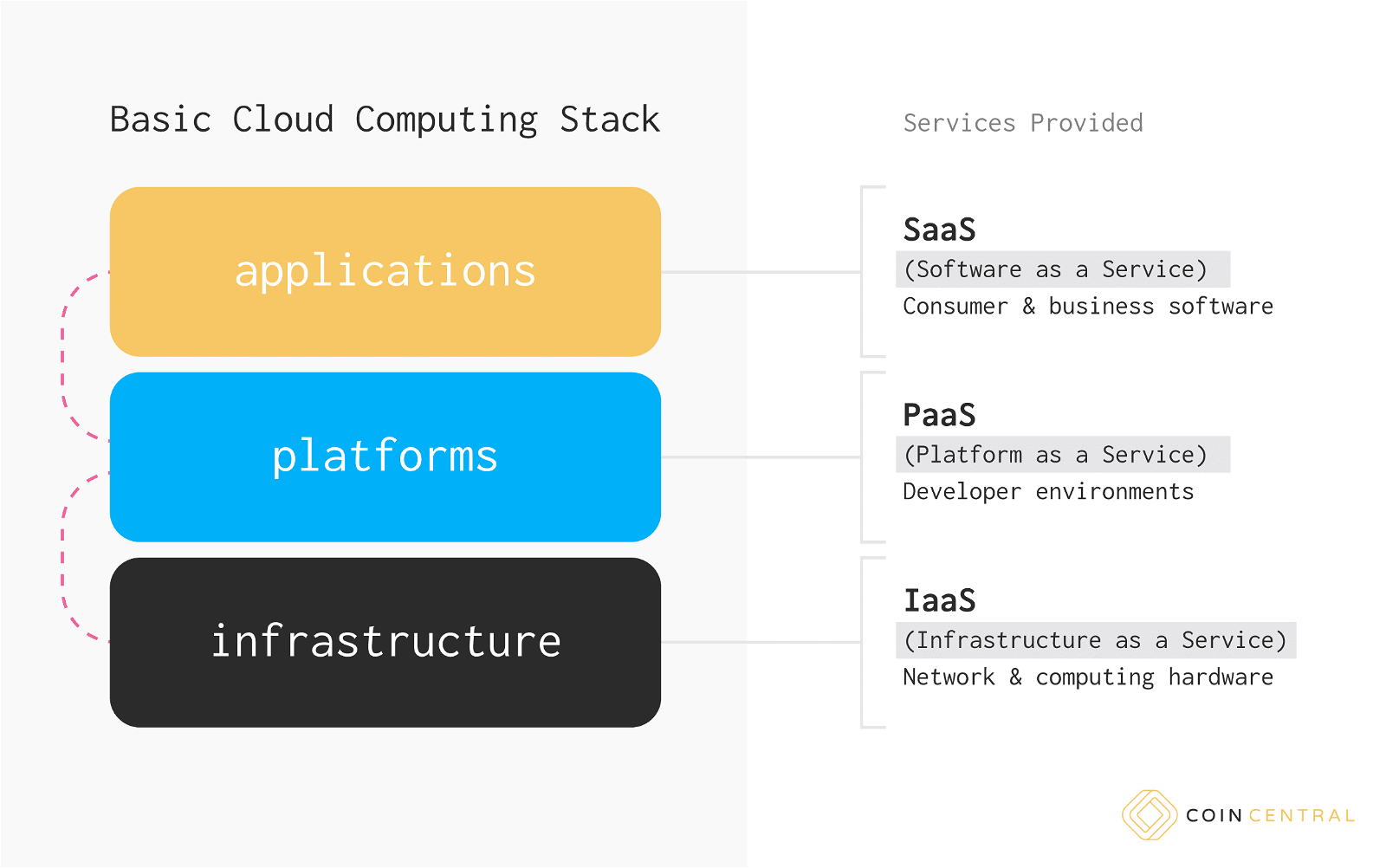
Cloud computing is really a stack of three generic cloud-provided services in any instance. Infrastructure cloud services, also known as infrastructure as a service, are at the bottom of the stack (IaaS). The developer layer, also known as platform as a service, is the intermediate layer (PaaS). The application layer, often known as the software as a service (SaaS) layer, is the top and most visible layer.
IaaS (infrastructure as a service) is the fundamental layer of the digital cloud, consisting of all the required hardware. Despite the allusion to a watery mist above us, cloud computing is built on actual, palpable, and frequently noisy technology. All of the actual hardware that stores and transfers our zeros and ones is referred to as IaaS.
CloudSigma, Digital Ocean, Linode, Cisco Cloud Infrastructure Services, Microsoft Azure, and Citrix Workspace Cloud are examples of IaaS providers.
The next tier up is PaaS (platform as a service), which is where the developers and programmers come in. IaaS providers lease pieces of cloud hardware to developers and programmers in this intermediate tier, which are pre-installed with development tools like Apache or MySQL. This is where IaaS providers and software developers meet in the intermediate layer.
Oracle Cloud, Salesforce Platform, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services are examples of PaaS providers.
The highest and most known tier of the cloud architecture is SaaS (software as a service). Here you’ll find apps and software, like Spotify, Adobe Creative Cloud, Google Play Store, Storj, and Dropbox, to mention a few. The SaaS layer is where cloud services for consumers and companies alike become more user-friendly.
Slack, WordPress, Trello, Mailchimp, InVision, Zoom, Buffer, Contently, and Netflix are some examples of SaaS providers.
The fundamentals of cloud computing
Each layer of the cloud service stack makes the previous layer possible. In a nutshell, the three levels are as follows: initially, you need hardware. Second, you’ll need a foundation on which to develop. Third, apps are required for users to be able to utilize the hardware.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Cloud Computing
While the benefits and downsides of cloud computing may vary depending on the use case, the following are some basic advantages and disadvantages.
Cloud Computing’s Benefits
- Access with Fewer Obstacles When opposed to developing and maintaining your own hardware, platform, or apps, cloud computing offers a far lower initial cost.
- There is much less waste. Cloud computing adapts to the needs of the user, whether large or little. If you just need 10 terabytes of storage, you should only pay for ten, and the storage may be scaled up or down as your requirements change.
- Take chances and try new things. Creators may be wrong more frequently and for less money with quicker scaling, iterations, hardware builds, and development environments, reducing the cost of success.
Cloud Computing’s Drawbacks
- A Catch-22 Situation in Security On the one hand, a cloud provider may be able to offer greater security management than you could alone. Centralizing your data to a cloud provider, on the other hand, provides additional incentives for security breaches.
- Lags in Performance It is possible that sharing infrastructure with other users will have an impact on its consistency. The amount of demand on the infrastructure may affect the amount of money you get. There are certain exceptions, but this is something to consider.
- Connection to the Internet In most instances, cloud computing requires an internet connection, which is unsurprising. There are numerous factors that influence how much data you need to transmit and how frequently you need to do so, but you can expect to be impacted by internet outages if they occur.
The Blockchain Could Be the Cloud’s Future
The next step in the development of cloud service stacks should be to include a distributed infrastructure layer. We may be able to alter the centralization of hardware and relieve that security vector by fragmenting smaller parts of a large cloud infrastructure.
If only there was a way to encourage hardware suppliers to collaborate in a distributed manner to offer cloud-like services to platform and software developers, the world would be a better place. If only it were that simple.
Cloud computing is a model of using shared resources to provide on-demand services that can be delivered over the internet. Reference: how does cloud computing work.
{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What is cloud computing outsourcing?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Cloud computing outsourcing is the process of using cloud computing services to manage your IT infrastructure.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What are the basics of cloud computing?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Cloud computing is a model of service delivery where companies rent time on remote servers from third-party providers to use as needed.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”What are the 3 basic components of cloud computing?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
The 3 basic components of cloud computing are the following:
-The Cloud is where your data is stored.
-The Cloud service provider manages the hardware and software resources in the Cloud.
-Cloud services enable organizations to use their existing IT infrastructure without needing to purchase new hardware or software.”}}]}
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cloud computing outsourcing?
Cloud computing outsourcing is the process of using cloud computing services to manage your IT infrastructure.
What are the basics of cloud computing?
Cloud computing is a model of service delivery where companies rent time on remote servers from third-party providers to use as needed.
What are the 3 basic components of cloud computing?
The 3 basic components of cloud computing are the following: -The Cloud is where your data is stored. -The Cloud service provider manages the hardware and software resources in the Cloud. -Cloud services enable organizations to use their existing IT infrastructure without needing to purchase new hardware or software.
Related Tags
- examples of cloud computing
- types of cloud computing
- cloud computing services
- cloud computing applications
- benefits of cloud computing